As of March 2023, Indian companies have parked over $5 billion in treasury Bills. These government-backed securities are a popular choice for businesses looking to save surplus funds in safe instruments.
In Today’s KOFFi break, let’s try to understand what treasury bills are and how they work.
What are Treasury Bills?
Treasury Bills also known as (T-bills) are Money Market instruments issued by the country’s federal bank to finance their short-term borrowing needs.
In India, the government issued these bills via the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) as a promissory note with a repayment guarantee to the investors after a specific period of time.
Since they are backed by the government of India, they are considered one of the safest short-term investments.
Why does the Government Issue Treasury Bills?
The government of India primarily issues treasury bills (T-bills) to raise short-term funds for their various expenditures and to manage cash flow. Here are the key reasons why the government of India issues treasury bills (T- bills):
- Raise Capital: By issuing treasury bills the government can borrow short-term debt from the public without spending on more expensive options like bank loans.
- Regulate Currency Circulation: The Reserve Bank of India uses treasury bills for an open market operation strategy to control liquidity and inflation in the economy.
During times of high inflation, the RBI can issue additional high-value treasury bills to absorb the excess liquidity and vice versa during economic slowdowns.
Benefits of Treasury Bills
- Risk-Free: Treasury bills (T-bills) are considered one of the safest short-term surplus fund parking as they are backed by the government of India.
- Guarantee Returns: When the treasury bills are issued by the Reserve Bank of India it comes with a guarantee from the government of repayment of the face value.
- Liquidity: Treasury bills ( T-Bills) are available in different maturity periods -14 days to 365 days which provide good liquidity to investors to access their money as per their requirements.
How do Treasury Bills (T-Bills) Work?
Reserve Bank of India (RBI) issues this government promissory note with a repayment guarantee to the investor under its open market operation (OMO) strategy for everyone to purchase.
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) conducts an auction for treasury bills (T-bills) on a weekly basis, typically on Wednesday.
Let’s try to understand it more deeply:
- Auction Calendar: The Government of India announces an indicative half-yearly auction calendar for treasury bills in consultation with the RBI.
- Press Release: Before each auction, the Reserve Bank of India issues a press release with the details of the treasury bill being issued.
- Minimum Investment: Individuals, companies, firms, trusts, and banks can participate in treasury bill auctions to invest money through commercial banks, primary dealers, or directly with RBI. The minimum investment amount is 25,000 and in multiples of 25,000 thereafter.
- Issuance: Treasury Bills are issued at a discounted price to their face value and investors receive the full face value when the T-bill matures.
For example, suppose a T-bill has a face value of Rs 98 and is available for purchase at a discounted price of Rs 100 at auction.
After the Maturity period, let’s say 91 days, is over, the government will purchase back the treasury bill from you at Rs 100, making a profit of Rs 2, which gives you a yield of 8.19%.
Yield =(100 – P)/P * 365/D * 100
Yield =(100 – 98)/98 * 365/91 * 100
Yield =8.19%
This difference between the discounted price and face value is the return earned by the investors.
Types of Treasury Bill
The type of treasury bills is mainly determined by the Maturity period and there are four main types of treasury bills issued by the Government of India based on their maturity period as listed below :
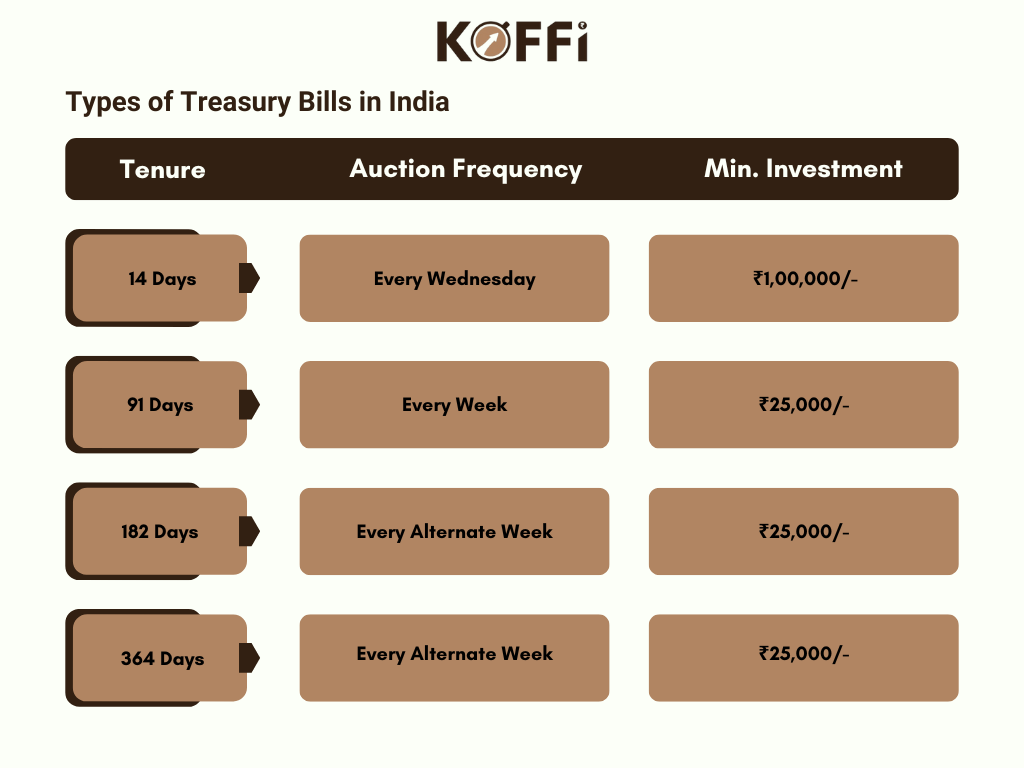
The maximum tenure of treasury bills is below one year. The tenure does not change for the treasury bills.
The face value and discount rates of treasury bills can change periodically based on the government funding requirements and RBI’s monetary policies.
Indian Government Incentive
The RBI launched a retail direct portal in November 2021 to facilitate retail investors to buy and sell government securities (G-Secs) directly on their smartphones. This portal enables retail investors to buy G-Secs in the primary auctions as well as buy and sell G-Secs in the secondary market.
This will open government securities doors for retail investors who want to park their funds in more secure instruments.
Things to Keep in Mind
The returns from treasury bills are subject to short-term capital gain tax (STCG) which is taxed as per the investor tax slab and can go upto 30 % depending on the applicable tax slab. This could further diminish the actual returns.
Treasury bills come with a minimum investment requirement of Rs 25,000 /- or Rs 1 lakh
Who should consider using Treasury Bills?
- Businesses: Businesses that are actively looking for better options to optimise their surplus funds.
- Safety Seeker: People who seek a safer option for parking their surplus funds for short-term
Final Thought
Treasury bills are promissory notes issued by the Reserve Bank of India and backed by the government of India which comes with a maturity period of up to one year.
These notes sold at a discount to their face value during the auction and repaid as per the original face value.
Treasury bills are an idle option for those looking for short-term surplus fund parking options instead of traditional bank deposits.
However, returns are taxable as per the investor’s applicable tax slabs.
Did you find this information valuable? Share this blog with someone who is actively looking for secure options for fund parking. Help them make informed financial decisions just as you do!
Was this helpful?
Click on a star to rate it!
As you found this post useful...
Follow us on social media!
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you!
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?


 Ask us Anything!
Ask us Anything!